The Polygon network, formerly the Matic network, is an Ethereum-scaling protocol that reduces cost and embeds high security. In a short span, Polygon has gained a high level of traction.
A string of solutions on a single network sets Polygon apart from other Ethereum scaling projects. It empowers developers to zero in on a scaling solution that works best with their applications. Polygon Labs has been consistently working to develop scaling solutions based on plasma sidechains, a blockchain bridge, different types of zero-knowledge proofs and Optimistic Rollups.
Processing bundles of transactions on the Polygon proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchain drastically reduces the burden on the Ethereum main chain, making transactions faster. The throughput rate in the Ethereum base layer is roughly 14 transactions per second, while Polygon has the potential to handle exponentially higher transactions per second.
Anyone wanting to participate in the network by updating transactional data on the system must stake Polygon (MATIC). In the Polygon network, a validator’s job is to ensure the network’s security and add transactions to blocks. Validators stake, allowing users to delegate tokens in exchange for rewards net of any commissions charged by validators.
Staking of MATIC, explained
Anyone looking to stake MATIC has to delegate tokens to a validator. Stakers can earn rewards against the staked funds. For now, there are no minimum staking requirements though validators can decide the minimum acceptable limit for staking. Validators might charge fees or commissions for these services. Staked MATIC tokens have an unlocking period of 80 checkpoints, approximately three to four days. Stakers wanting to exit just need to send an unbound request.
It helps to factor in validators’ credibility before delegating funds to any of them. One can hop to the Polygon staking dashboard to get information about validators, viewing metrics such as active validators, their uptime, commission and the amount required to stake. These metrics are valuable tools to help select reliable validator(s):
- Uptime refers to the number of blocks signed in a specific time period. A validator’s uptime should be close to 100%. Otherwise, it indicates the validator is unreliable, as reflected in their public performance metrics.
- Commission rate is the percentage of one’s rewards the validator receives for their services.
- The stake amount indicates the total number of tokens delegated to a validator.
How to stake MATIC on MetaMask
MetaMask is a decentralized, noncustodial cryptocurrency wallet that interacts with the Ethereum blockchain. The wallet is accessible as a mobile app and browser extension on Google Chrome, Brave, Firefox, Opera and Edge.
Here are the steps to stake MATIC on MetaMask:
Step 1: Add MetaMask as a browser extension.
To stake MATIC on MetaMask, users need to visit the MetaMask website and set it up as a browser extension. Go to “Download.” One can choose between the currently used browser and iOS or Android. Select the download option for the browser to add MetaMask.
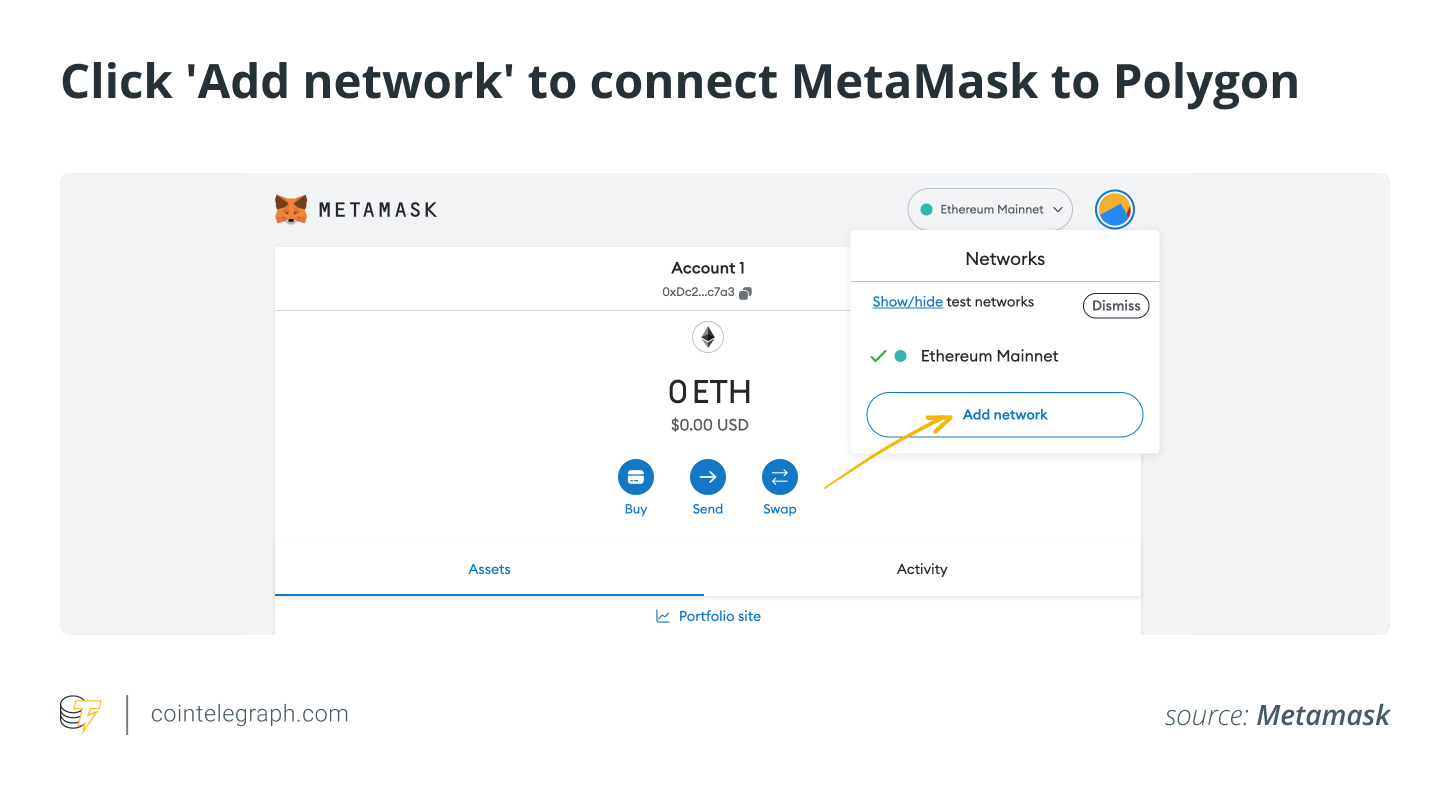
Step 2: Connect MetaMask to the Polygon blockchain.
MetaMask is compatible with different blockchains. To connect MetaMask to Polygon, go to “Networks” and “Add network.” In the window that appears, users must populate relevant data regarding the Polygon blockchain.
Step 3: Transfer MATIC tokens to MetaMask.
To transfer MATIC tokens to the MetaMask wallet, copy the address from the wallet and feed it in as the destination address on the exchange or another wallet. Now, transfer MATIC tokens to MetaMask.
Step 4: Connect MetaMask to the Polygon Wallet.
On the following link, click “MetaMask” to connect MetaMask to the Polygon wallet. https://wallet.polygon.technology/
Step 5: Stake MATIC via MetaMask.
Once the connection is established, staking is enabled.
Step 6: Delegate MATIC.
Select a validator to which tokens will be delegated.
One needs to use the control panel for staking. Click on the button “Apps” and then select “Staking.” Put the validator’s name in the search bar and click “Delegate.” All relevant information, such as the number of tokens staked, uptime and commission amount, is visible next to the validator’s name.
Feed in the MATIC amount for staking and click “Continue.” In the pop-up extension window, click “Confirm.” The transaction might take a few minutes to complete, depending on traffic.
To execute a transaction, stake MATIC and begin receiving rewards, users must buy a voucher and pay for gas. Click “Buy Voucher.” Specify details like the gas limit and price, and re-confirm the transaction.
Delegation is now complete. Users can “Stake more” or withdraw the rewards using the control panel. However, note that all transactions on the Ethereum network are paid in Ether (ETH). Therefore, the delegator must have enough ETH in the wallet to pay for the transactions.
How to stake MATIC on Coinbase Wallet
To stake MATIC on Coinbase, users need to use a wallet, as they don’t provide a staking feature on the exchange. If users have funds on the exchange but not in the wallet, they will need to move funds to the wallet. Even though Coinbase Wallet doesn’t have a built-in staking feature, there is a way to do it.
Here are the steps leading to staking MATIC on Coinbase Wallet.
Step 1: Install Coinbase wallet.
Install Coinbase Wallet on your smartphone. If it is an iPhone, go to the Apple App Store; visit the Play Store for Android.
The process includes creating a new wallet, agreeing to the terms of service, picking a username, setting privacy preferences, creating a passcode and backing up the wallet with a recovery phrase to help access the account in case users forget the passcode.
Step 2: Move funds to the wallet.
Open the wallet and go down to the bottom right. Tap there and scroll down the screen that appears. The link “Connect to Coinbase” will be visible. Hit the link, and it will ask for authorization. Once done, the wallet will establish the user’s connection to their wallet.
Hit “Buy or transfer.” When the exchange prompts you to select a coin, select “MATIC wallet.” Now, users can feed in the number of coins they want to transfer. The wallet will ask for a verification code. Once successfully deposited, funds will be transferred. MATIC tokens on Coinbase exchange are ERC-20 tokens, meaning they run on top of the Ethereum network.
Step 3: Stake MATIC.
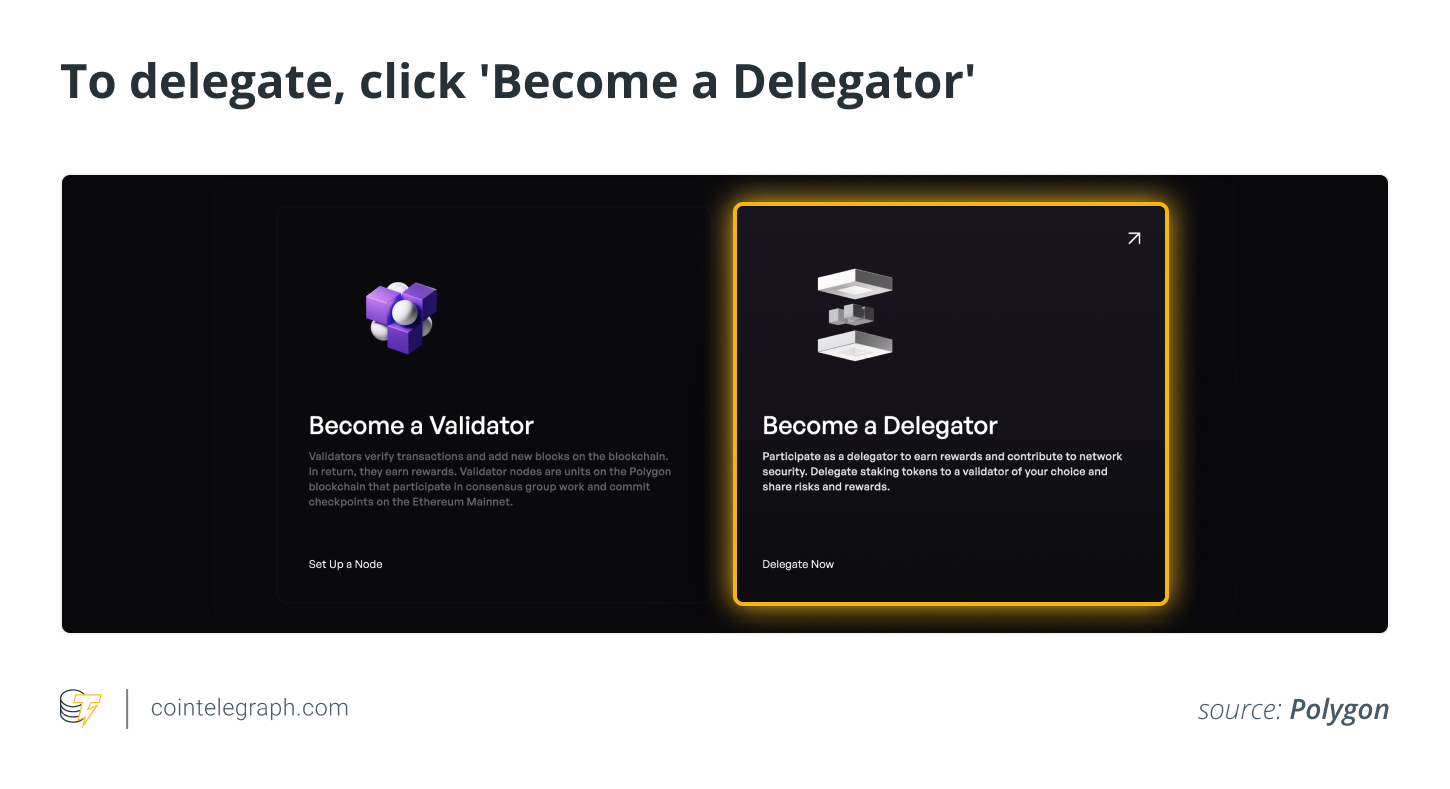
Visit the Polygon website. On the top menu, click “Use Polygon” and “Staking.” On the next page, click “Become a delegator.”
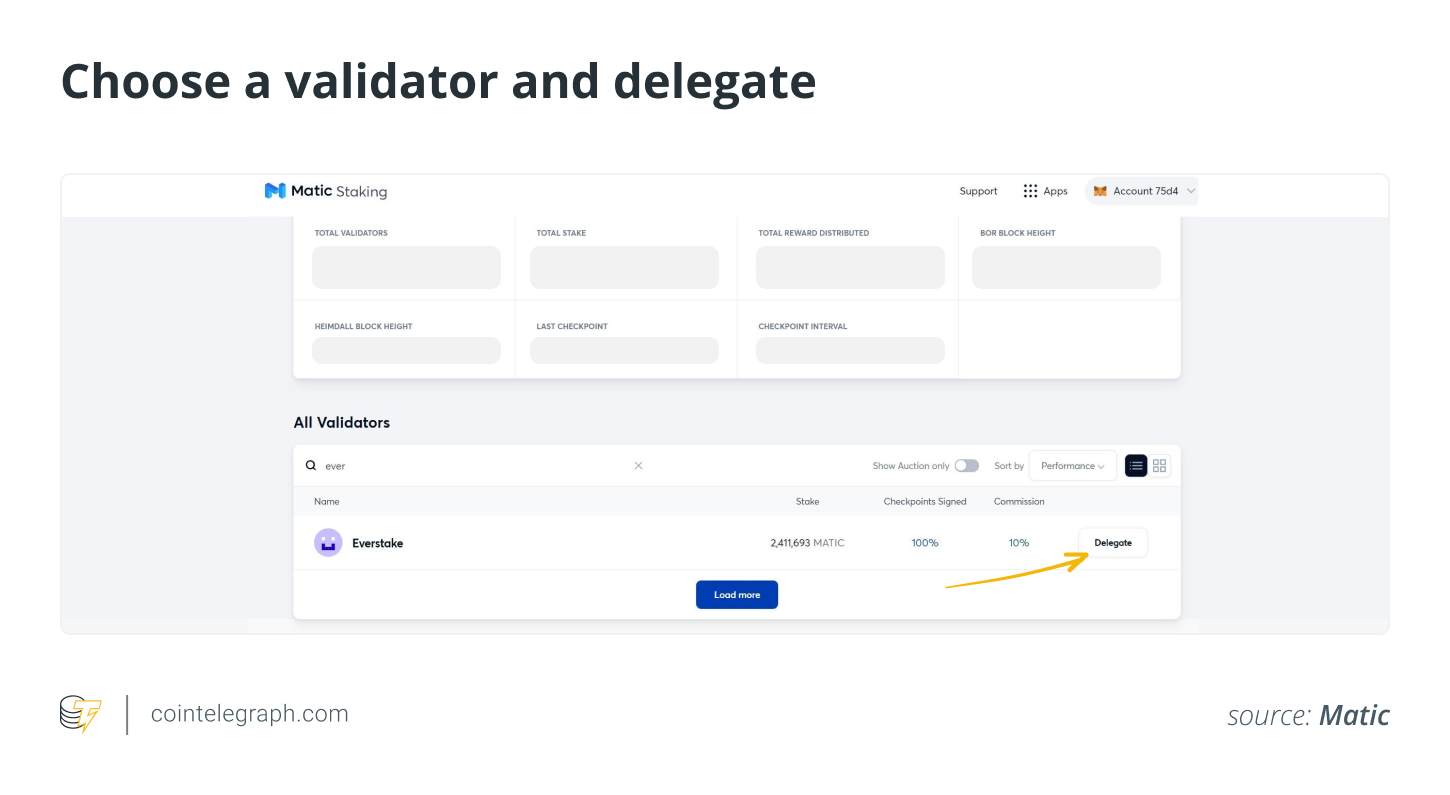
The user is taken to a page displaying a list of validators and their relevant details. One can sort the list in line with four parameters: performance, commission, stake and random, by clicking a drop-down list on the right of the page. The user can view the validators as a grid or a list. They can also search for a specific validator using a search box on the left.
When users click any of the validators, they are taken to the page displaying further details of the relevant validator, such as MATIC staked, the commission asked, checkpoints signed and health status. Users can go through the list and click any validator.
A different page displays further details of the validator. This includes the amount of MATIC their Ethereum wallet balance holds and its value in dollars, their stake, heimdall fee, rewards earned, performance index, checkpoints signed and more. Heimdall fees refer to the fees the validator has to pay using the Polygon network to submit checkpoints.
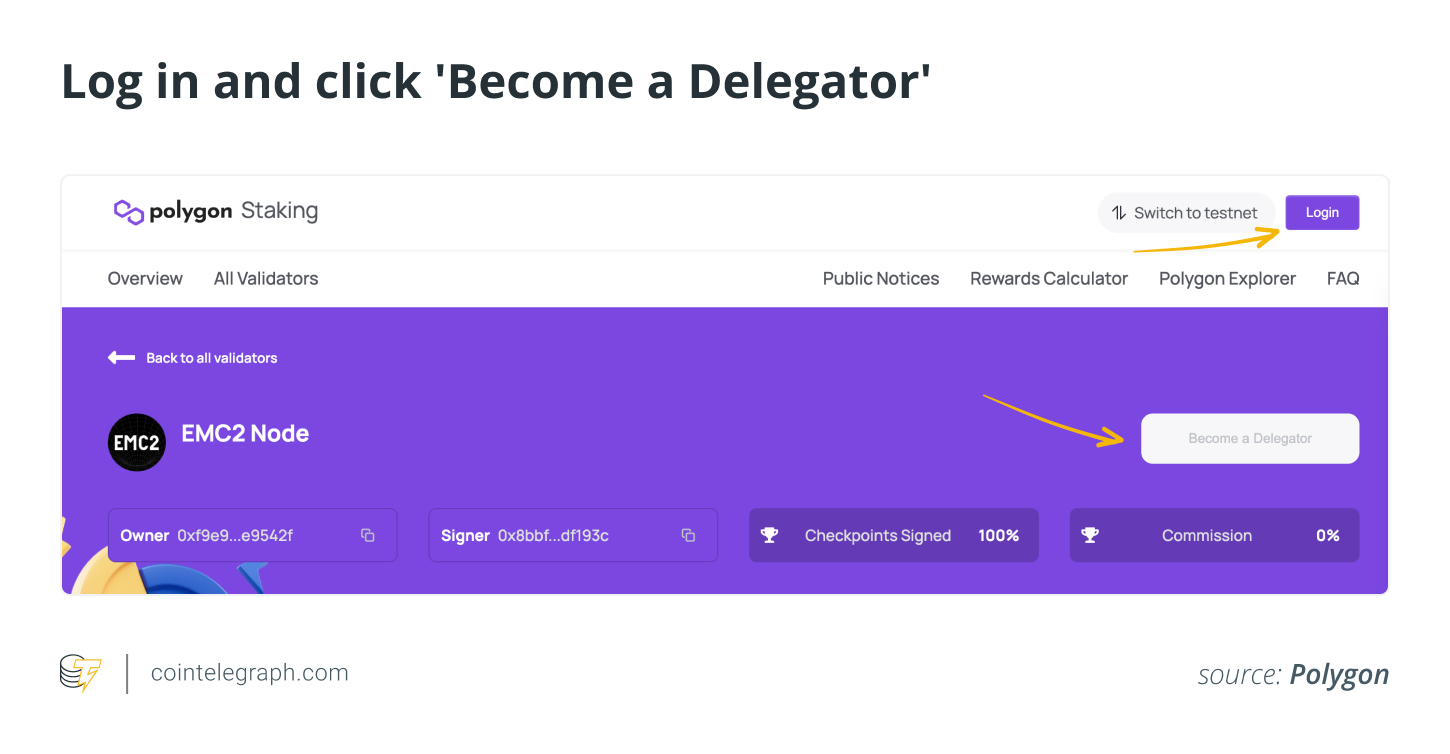
The user must log in by clicking the button at the top-right using their credentials. Users without an account on Polygon must create one and click the “Become a Delegator” button.
Users need to populate the number of MATIC coins they intend to delegate and tap “Continue.” When the user clicks “Continue,” a pop-up appears. The user must tap the “Delegate” button to complete the process.
How to stake MATIC on Trust Wallet
Trust Wallet is a decentralized, noncustodial mobile app wallet for storing, exchanging and transferring crypto assets. Here is the process to stake MATIC on Trust Wallet:
Step 1: Set up a Trust Wallet.
Set up a Trust Wallet on your mobile phone. Select the preferred operating system (iOS or Android) and install the app.
If users have already been using Trust Wallet, they must import the wallet. Otherwise, they have to set up a new wallet. To import an existing wallet, click the “I already have a wallet” button and confirm a six-digit passcode.
If a user is uninitiated with the wallet, they must read and agree to the privacy policy and terms of service, create and confirm a six-digit passcode and back up the wallet with a recovery phrase.
Trust Wallet allows a wallet for several coins, but a multicoin wallet is usually the most suitable. As MATIC staking occurs on Ethereum, one requires an adequate amount of ETH and MATIC on the Ethereum mainnet.
Step 2: Connect Trust Wallet to Polygon.
Log in to the Polygon staking dashboard and click “Become a Delegator.” From the list of wallets, select “WalletConnect” to connect to Trust Wallet on Polygon. A QR code will appear on the screen.
Return to the Trust Wallet app, go to the settings and choose WalletConnect. Click the “New Connection” button. Scan the QR code on the Polygon staking dashboard. Click “Confirm” to establish the connection.
Step 3: Delegate and approve transaction.
Select the validator and click “Delegate.” Feed the number of MATIC coins to be staked and click “Continue.” To approve the transaction, confirm the smart contract call in the Trust Wallet app.
Get back to the Polygon staking dashboard and click “Delegate.” Confirm yet another smart contract call in the Trust Wallet app. Delegation is active and users can begin accruing rewards.
How to stake using Ledger
Ledger is a popular device for storing cryptocurrencies. Before staking MATIC with Ledger, one needs to prepare for it.
Step 1: Prepare for staking.
The process starts with updating Ledger Live to the latest version using the link: https://www.ledger.com/ledger-live/download
Connect the Ledger device to “My Ledger” and install the latest version of the ETH app on the Ledger device. Enable blind signing in the ETH app settings. When the preparation process is completed, Close Ledger Live or problems might arise when working with MetaMask.
Users also need to ensure MATIC is stored in the Ledger Ethereum account and not in the Polygon account, as MATIC staking happens on the Ethereum network.
Step 2: Connect Ledger ETH account to MetaMask.
Connect the Ledger device to the desktop and open the ETH app within. Now, link the Ledger ETH account to MetaMask.
Once the connection is established, go to the Polygon Wallet app.
Connect your Ledger Ether account to MetaMask by following these steps.
Once done, go to the Polygon Web Wallet app, select “Connect to a Wallet” and then MetaMask.
When MetaMask opens in the browser, select the Ledger account, click “Next” and then “Connect.” Ledger displays “Sign message.” Select “Sign message” and simultaneously press both buttons to confirm. Now, MetaMask is connected to the Polygon Wallet app.
Step 3: Select a validator.
Select “Polygon Staking.” In the app’s top-right corner, click the “Login” button and select MetaMask again.
Choose a validator from the list that appears. Users need to consider two parameters: a high score for “Checkpoint signed” and a low “Commission.”
Step 4: Delegate.
Click the “Delegate” button, fill in the amount of MATIC to be staked and click “Continue.” MetaMask displays “Give permission to access your MATIC?”
Review the fee amount; if it looks satisfactory, click “Confirm.” Ledger now displays “Review transaction.”
Select “Accept and send” and press both buttons simultaneously to “sign the transaction.” Ledger now displays “Application is ready.”
Return to the Polygon Web Wallet App, select a validator and click “Delegate.”
Review and confirm the transaction through MetaMask and Ledger devices. When the Ethereum network confirms the transaction, the screen will display “Delegation Completed.”
How to stake MATIC using ZenGo wallet
ZenGo is a self-compatible wallet. It’s compatible with WalletConnect, with no seed phrase vulnerability. Let’s go through how users can stake MATIC using a ZenGo wallet.
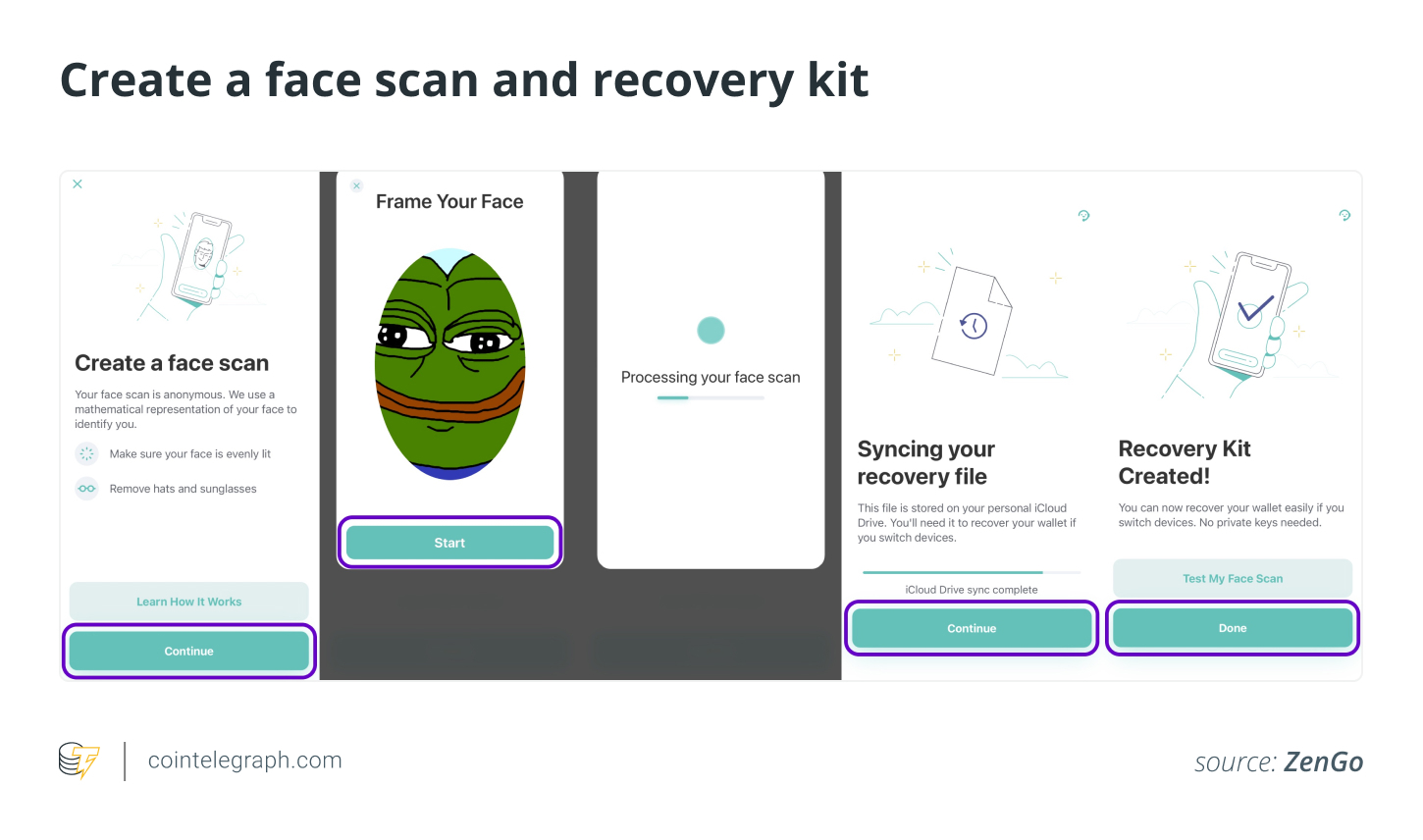
Step 1: Install the ZenGo wallet on your mobile phone.
Visit the ZenGo website, select an operating system (iOS or Android) and install the app on the mobile phone. To accelerate the search, one can scan the QR code.
Open the ZenGo app, enter an email address and tap “Continue.” ZenGo requires the user to confirm their email address. For confirmation, reach the inbox by tapping “Open My Email” in the ZenGo app, then tap “Tap to Confirm” in the email received. After email address verification, enable biometrics to make the app even more secure.
Create a Recovery Kit for the safety of funds and easy access when changing devices. As a noncustodial wallet, ZenGo shares an encrypted secret key share. Part of the key stored on the device helps unlock the wallet and use it with a face scan. Once the Recovery Kit is created, tap “Done.”
Step 2: Connect ZenGo wallet to Polygon.
Users need to connect the ZenGo wallet to Polygon. Open the link https://staking.polygon.technology/
Go to the Polygon staking dashboard. In the upper right part of the screen, tap “Login.”
Tap WalletConnect from the list of available connections. WalletConnect protocol enables one to connect ZenGo to Polygon. The QR code will appear.
Go to the ZenGo wallet homepage and tap the “Connect to Apps” button in the upper right corner. Scan the QR code.
Step 3: Select a validator and delegate MATIC.
Now begins the process of delegating MATIC. Make sure to have MATIC in ERC-20 and 0.05–0.1 ETH for fees, as the delegation happens on the Ethereum mainnet.
On the Polygon staking dashboard, scroll down to find information such as the network’s overview, active validators, their amount of stake, uptime, commission, amount of stake and health metrics.
Select a validator after considering the metrics and tap “Delegate” at the bottom-right of the screen.
In the pop-up box that appears, users need to enter the amount of MATIC to be staked and tap “Continue.” You can stake with an amount as low as 1 MATIC. To confirm the transaction, return to the ZenGo app and approve the transaction in the pop-up window.
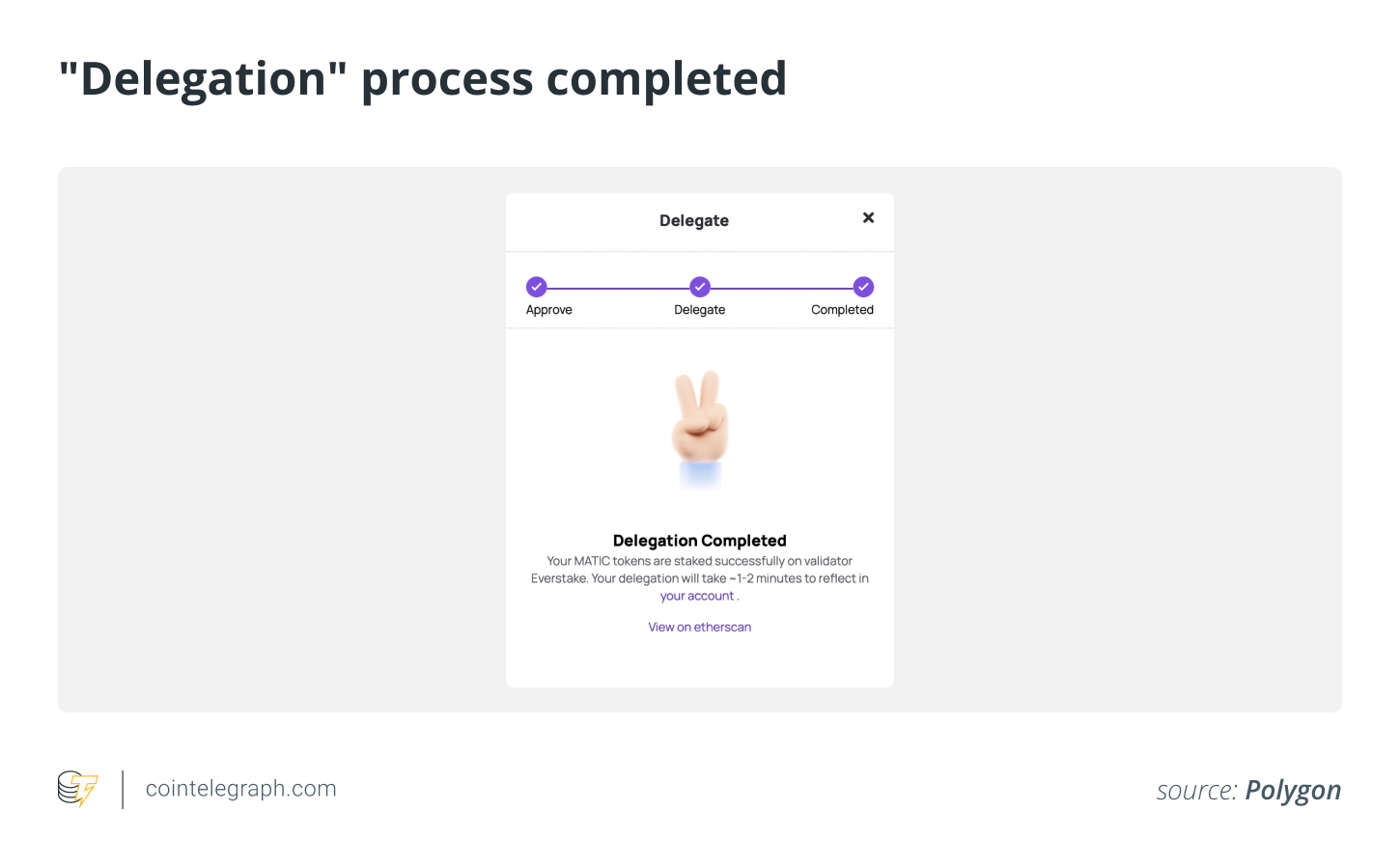
Revisit the Polygon staking dashboard and tap “Delegate.” In the ZenGo wallet, confirm the transaction and wait for approval.
Once delegation is active, the user will begin receiving rewards. At each checkpoint, rewards get accrued.
Rewards are received in the “My Account” section of the Polygon staking dashboard. Users can also unstake, stake to multiple validators or restake funds. To withdraw the rewards accrued, users must have a minimum of 2 MATIC in their account.
The road ahead
As a prominent layer-2 network, the Polygon protocol is a solution that helps Ethereum expand in size, security, efficiency and use cases. As the unit of payment and settlement in the network, MATIC helps power the system. The Matic network went live in 2020, rebranded to Polygon in February 2021, and is being used by developers to build Ethereum-compatible decentralized applications.
The Polygon protocol has been instrumental in making Ethereum usable and pulling it out of the mess the blockchain found itself in after rapid growth. Transactions were stuck for hours over a lack of scalability, with the cost of executing transactions often more than the transaction amount itself. The Polygon protocol has effectively transformed Ethereum into a full-fledged multichain system with the advantages of Ethereum’s decentralization and vibrancy.
MATIC token is here to stay and keeps playing an increasingly important role in retaining the functionality of Ethereum ecosystem. Staking, meanwhile, will serve as a mechanism to ensure proper governance and security of the network.