The world of blockchain gets so many new projects that it’s easy to forget the ones that that fizzled out.
Whereas every new “Ethereum killer” gets attention, as do disaster projects like HashOcean and BAS, it’s important to look back in time to some older projects (that means over 2 years plus, in crypto) that generated huge hype which never translated to results.
These are not scams or complete failures, but projects that never quite lived up to their hype.
By looking at these, you’re reminded that in an emerging, volatile industry like crypto, even large, highly-anticipated projects don’t always go as planned.
Bitcoin Cash
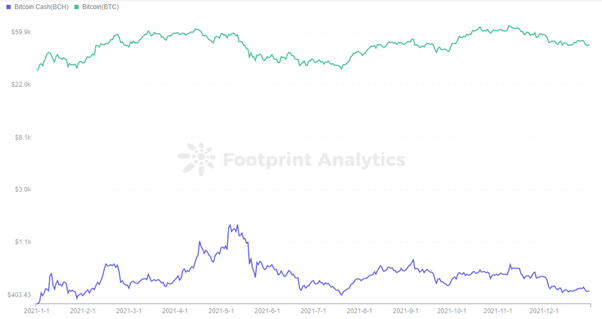
Bitcoin Cash, or BCH, is both a payment network and a cryptocurrency. As of March 9, the 27th largest cryptocurrency by market cap. BCH was launched in August 2017 as a hard fork of the Bitcoin blockchain.
It reached an all-time high on December 23, 2017, at $3,923. Its price has largely maintained similar fluctuations to BTC.
Footprint Analytics – Price of BTC and BCH
Bitcoin Cash was forked to increase Bitcoin’s 1M block limit and has now reached a max of 32M blocks. Therefore, per transaction processed speed is much higher than BTC, and transaction fees are lower. But Bitcoin Cash can’t beat BTC in terms of market cap for now.
Why it didn’t work
BCH is still the primary crypto for decentralization, cross-border transactions, and continues to evolve as a store of value. It has now become analogous to digital gold, with the payment function fading away.
Digital gold is more valuable than a means of payment. BCH is unable to surpass BTC because of its positioning, as iron is less than valuable than gold.
BCH was also affected by the Fed’s interest rate hike, balance sheet reduction, and the fall of US stocks. The best time to surpass BTC has been missed.
With a new bear market on the horizon and negative political factors, there could be a new wave of downward pressure on BTC.
However, BCH still has an active community that believes it could make a rebound and become the next big thing, as evidenced by Bitcoin Cash’s Reddit community.
Ethereum Classic
Often mentioned alongside BTC, ETH has its sister, Ethereum Classic. Even though it is a network with ETH technology and BTC concept, it has not shaken Ethereum’s position.
Ethereum’s hard fork occurred in July 2016, when founder Vitalik Buterin proposed the idea of a hard fork. To recover the assets stolen by hackers from the DAO. Eventually, Ethereum forked into Ethereum and Ethereum Classic.
Ethereum Classic, ETC, is ranked 34th in cryptocurrency market capitalization. The fork keeps the vision and philosophy of the original Ethereum, with a higher degree of decentralization and community autonomy, but with only 15% HashRate support.
Nowadays, both the token price and ecosystem applications are far less than Ethereum.
Why it didn’t work
From the hard fork, the original Ethereum founders and team left to go support and lead the current Ethereum, while Ethereum Classic was taken over by a new team.
In terms of supporters, with 85% HashRate support after the fork, Ethereum has far more supporters and higher demand than Ethereum Classic.
In terms of ecosystem integrity, Ethereum has become the top public chain TVL, while not many projects are deployed on Ethereum Classic.
So, in many ways, even though Ethereum Classic is more committed and decentralized, it didn’t end up being the dominant player in the blockchain world.
NEO
NEO, formerly AntShares, was launched in China in 2014 by Erik Zhan and his team as a public chain. It was an open-source project in 2015 on Github and completed ICO capitalization a few months later.
NEO supports the development of its own cryptocurrency, digital assets, and smart contracts that can achieve thousands of transactions per second.
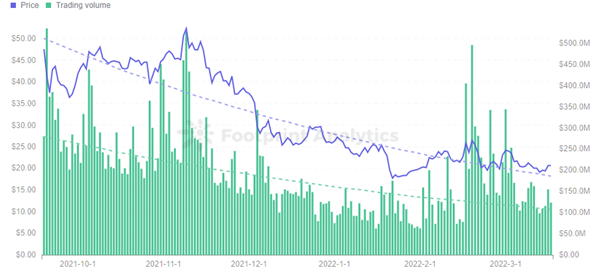
Neo’s price has risen very sharply. From $0.08 at launch, it reached an all-time high of $198.38 on January 15, 2018, an increase of 2,478.75%.
But it was short-lived, and the overall downward trend is evident in Footprint Analytics data, with the current price at $21.27.
Footprint Analytics – Price & Trading Volume of Neo
Why it didn’t work
The former 1,000x coin has fallen, becoming the 77th largest coin in terms of market capitalization. This is not due to objective off-site factors such as the poor performance of the cryptocurrency market, but rather NEO itself.
- Code updates of NEOs are weak
- Ecosystem development is almost stagnant.
- Decentralization is weak. There are only 7 voting nodes and they are officially deployed by NEO.
As the saying goes, if the foundation is not strong, the ground will shake. If NEO fails to address the above issues, it will continue to be overtaken in a new bear market.
EOS
In May 2017, block.one launched EOS as a smart contract platform and distributed operating system. It became a strong competitor to Ethereum in 2018.
At that time, the market was skeptical of Ethereum due to transaction congestion, high gas fees, and failure to release its sharding technology.
After launching in less than 6 months, EOS—with zero fees and extremely fast transaction speeds—crashed Ethereum’s less than 3,000 daily transactions with a single-day count of 30,000. EOS was the OG Ethereum-killer.
Why it didn’t work
However, the young protocol ultimately failed to live up to its potential. EOS’s extremely fast transaction processing comes at the expense of decentralization.
EOS’s consensus mechanism has 21 supernodes to process transactions, making it impossible for smaller node operators to participate. Supernodes are elected by holding coins, with the implied risk of bribery.
Ethereum and Bitcoin’s POW consensus mechanism is inefficient, while EOS’s Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism is very efficient.
Yet, the core of blockchain is decentralization, and EOS is essentially more of a centralized chain.
Currently, almost all active top public chains have impressive applications or at least have protocols that support public chains. For example, Anchor on the Terra chain. However, EOS did not.
Although EOS officials have repeatedly said that they support ecosystem construction, as of March 9, the on-chain ecosystem of EOS still looks like a barren wasteland.
Dfinity / Internet Computer
Dfinity is a decentralized cloud technology platform. Founded in 2016, it was quite popular with venture capitalists. It bucked the bear market in 2018 and received $102 million in funding from a16z, the largest outbound investment by a16z that year.
Dfinity’s vision is to create a public cloud computing platform that is more efficient and secure than AWS, putting the blockchain network under the control of a distributed computer network.
The Internet Computer was expected to launch in the second half of 2018 or the first half of 2019, but the actual Alpha master network went live in December 2020.
Why it didn’t work
Dfinity has taken more than two years since its funding to deliver a product and it is not unique. The team moves too slowly.
In terms of blockchain AWS solutions, Alchemy, a blockchain development platform service for Web3, was founded in 2017 and powers most of the world’s blockchain companies today.
For source code, Github has been around since 2008 and is the platform where the vast majority of today’s blockchain protocols are hosted.
Community autonomy, which allows the community to manage tokens, has also been implemented in many projects.
While the concept of Dfinity is interesting, the delayed launch caused the project to lose its thunder.
This piece is contributed by the Footprint Analytics community.
The Footprint Community is a place where data and crypto enthusiasts worldwide help each other understand and gain insights about Web3, the metaverse, DeFi, GameFi, or any other area of the fledgling world of blockchain. Here you’ll find active, diverse voices supporting each other and driving the community forward.