What is a supply chain attack in crypto?
A supply chain attack in the crypto domain is a cyberattack where hackers target third-party components, services or software that a project relies on instead of attacking the project itself. These components may include libraries, application programming interfaces (APIs) or tools used in decentralized applications (DApps), exchanges or blockchain systems.
By compromising these external dependencies, attackers can insert harmful code or gain unauthorized access to critical systems. For instance, they might alter a widely used open-source library in DeFi platforms to steal private keys or redirect funds after it is implemented.
The dependence of the crypto ecosystem on open-source software and third-party integrations makes it highly susceptible to such attacks. Such attacks in crypto exploit weak entry points such as compromised Node Package Manager (NPM) or GitHub dependencies, where attackers inject malicious code into widely used libraries.
Hardware wallets or SDKs can also be tampered with during manufacturing or updates, exposing private keys. Moreover, attackers may breach third-party custodians or oracles, manipulating data feeds or wallet access to steal funds or disrupt smart contracts across decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms.
Did you know? Some attackers host clean code on GitHub but publish malicious versions to PyPI or npm. Developers trusting the GitHub repo may never suspect that what they are installing is different and risky.
Malicious supply chain attacks targeting crypto projects
In 2024, attackers increasingly used open-source software (OSS) repositories to launch supply chain attacks aimed at cryptocurrency data and assets. Their goal was to trick developers into downloading harmful packages.
According to Reversing Labs’ “2025 Software Supply Chain Security Report,” OSS platforms used for attacks included npm and PyPI. Here are the associated details:
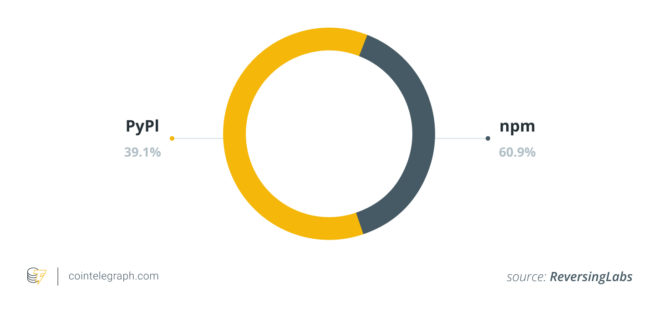
- Targeted repositories: Attackers uploaded malicious code to two widely used OSS platforms, npm and Python Package Index (PyPI).
- Campaign count: ReversingLabs (RL) reported 23 crypto-related campaigns in total.
- npm focus: Out of the campaigns launched, 14 were on npm, making it the most targeted.
- PyPI Cases: The remaining nine campaigns occurred on PyPI.
There are varying levels of sophistication in attacks. Campaigns could range from basic, well-known methods to more advanced, stealthy approaches. Typosquatting is a common technique used in supply chain attacks where malicious packages closely mimic legitimate ones.
Examples of supply chain attacks in crypto
This section examines four real-world instances of supply chain attacks in crypto, revealing attacker methods and crucial lessons for enhancing security:
Bitcoinlib attack
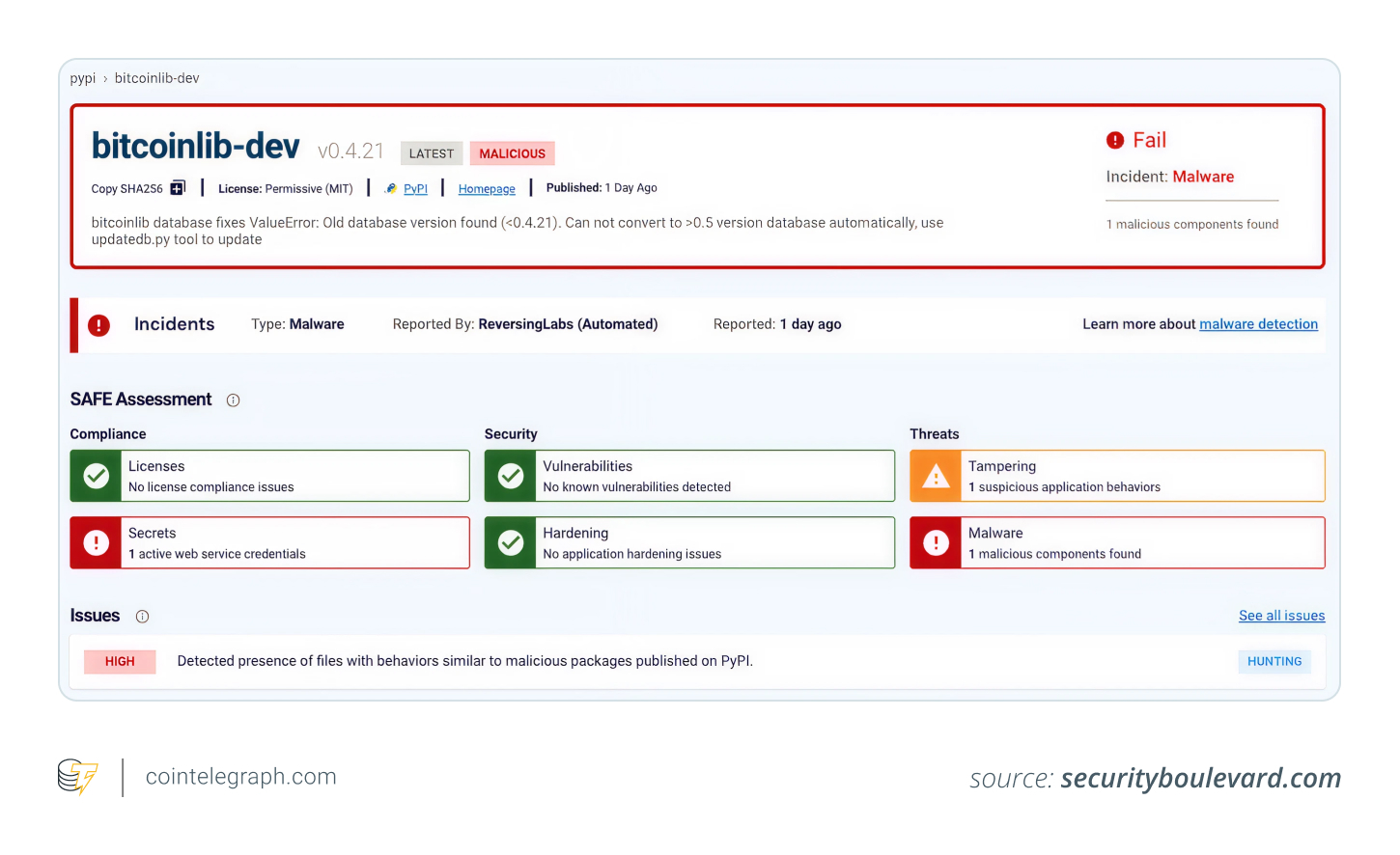
In April 2025, hackers targeted the Bitcoinlib Python library by uploading malicious packages, “bitcoinlibdbfix” and “bitcoinlib-dev,” to PyPI, posing as legitimate updates. These packages included malware that replaced the command-line tool “clw” with a version that stole private keys and wallet addresses.
Once installed, the malware sent sensitive data to attackers, enabling them to empty victims’ wallets. Security researchers detected the threat using machine learning, preventing further harm. This incident emphasizes the dangers of typosquatting attacks in open-source platforms and the need to verify package authenticity before installation.
Aiocpa long-term exploit
The “aiocpa” exploit was a complex supply chain attack targeting cryptocurrency developers through the Python Package Index (PyPI). Launched in September 2024 as a legitimate Crypto Pay API client, the package gained trust over time. In November, version 0.1.13 introduced hidden code that stole sensitive information, such as API tokens and private keys, sending it to a Telegram bot.
The malicious code was not present in the GitHub repository, bypassing typical code reviews before it was detected by machine learning tools, leading to the quarantining of the package. This incident highlights the need for careful dependency management and advanced threat detection in open-source platforms.
The @solana/web3.js supply chain attack
In one of the most notorious supply chain attacks in 2024, malicious actors compromised the @solana/web3.js package, a widely used JavaScript API for interacting with the Solana blockchain. Attackers injected harmful code into versions 1.95.6 and 1.95.7, aiming to steal sensitive user information.
The package, with over 3,000 dependent projects and 400,000 weekly downloads, was an ideal target due to its widespread use. This incident demonstrated how even trusted, high-profile packages can become attack vectors, posing significant risks to developers and users across the crypto ecosystem.
DNS hijack of Curve Finance
In 2023, Curve Finance suffered a DNS hijack through its domain registrar. Attackers compromised the registrar account and altered the DNS records, redirecting users from Curve’s official website to a malicious clone site. While the backend smart contracts remained secure, users who accessed the spoofed frontend unknowingly approved transactions that drained their wallets.
This incident highlighted a major vulnerability in DeFi: Although blockchain infrastructure is secure, reliance on centralized web services like DNS creates weak points ripe for exploitation.
Did you know? In a supply chain trick called dependency confusion, attackers upload fake internal packages to public registries. If a developer’s system installs the wrong version, attackers gain a backdoor to their crypto apps.