The Ethereum network recently underwent the Arrow Glacier hard fork on Dec. 9, with the sole purpose of delaying the “difficulty bomb” to June of next year. The difficulty bomb is a mechanism to force the proof-of-work network to stop producing blocks, making mining unprofitable and disincentivizing miners from keeping the chain alive after the network merges to proof-of-stake.
Ethereum core developers have made significant progress toward the Merge, with client interoperability and a functioning developer network, Amorpha. However, more time is needed to deliver the mainnet level change to proof-of-stake.
While this marks the fourth time that the difficulty bomb has been delayed, core developers have signalled almost unanimous confidence that the Merge will be ready by next summer, and they will continue to provide updates during weekly All Core Developers meetings.
Welcome to another edition of Valid Points.
Pulse check
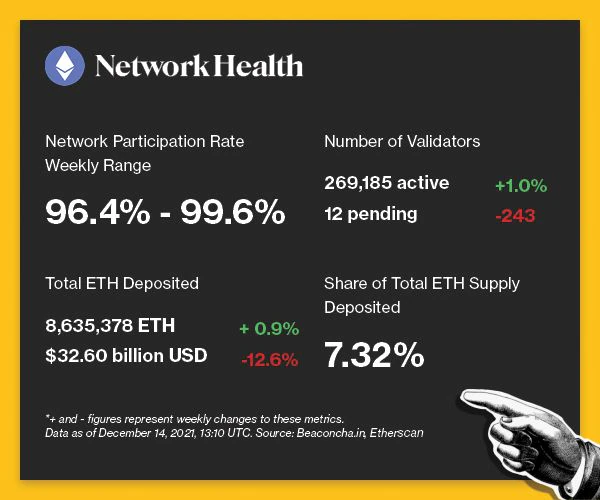
The following is an overview of network activity on the Ethereum 2.0 Beacon Chain over the past week. For more information about the metrics featured in this section, check out our 101 explainer on Eth 2.0 metrics.
Disclaimer: All profits made from CoinDesk’s Eth 2.0 staking venture will be donated to a charity of the company’s choosing once transfers are enabled on the network.
Validated takes
Optimism announced the removal of its application whitelist, allowing developers to build on top of the rollup. BACKGROUND: Optimism, a highly anticipated Ethereum layer 2 protocol, used a controlled launch with only select applications several months back. “Opening the floodgates” to all developers signals high confidence in Optimism’s safety and user experience.
DeFi showed resilience during the recent pullback across crypto markets, with only a tiny portion of loans getting liquidated on platforms like Aave and Compound. BACKGROUND: DeFi is often thought of as risk-on and a means of getting cheap leverage. However, on-chain liquidations were just a drop in the bucket compared to the wipe on centralized exchanges. A Delphi Digital analysis showed a majority of loans on Aave and Compound used very low leverage.
The Ethereum Foundation announced a grant that would award high-functioning client teams with Beacon Chain validators. BACKGROUND: A diverse range of high-quality clients is vital to the success of Ethereum, so that the network can maintain health even if one client runs into a bug, since the rest will still be running smoothly. In order to align the network and client teams in the long run, the Ethereum Foundation announced it would give 144 vesting validators to each client team to run with their respective software.
Polygon moves closer to bringing EIP 1559-style fee markets to their proof-of-stake scaling platform. BACKGROUND: Internal analysis showed that the fee burn would remove 0.27% of Polygon’s total supply annually. Unlike Ethereum, Polygon has a fixed supply and will immediately become deflationary when the upgrade takes place on mainnet. Outside of burning token supply, the upgrade will help bring predictability to the Polygon fee market, and software providers will be better able to predict acceptable transaction fees.
Open comms
Valid Points incorporates information and data about CoinDesk’s own Eth 2.0 validator in weekly analysis. All profits made from this staking venture will be donated to a charity of our choosing once transfers are enabled on the network. For a full overview of the project, check out our announcement post.
You can verify the activity of the CoinDesk Eth 2.0 validator in real time through our public validator key, which is:
0xad7fef3b2350d220de3ae360c70d7f488926b6117e5f785a8995487c46d323ddad0f574fdcc50eeefec34ed9d2039ecb.
Search for it on any Eth 2.0 block explorer site.